Ecommerce Jargon: The 48 Most Commonly Used Terms (Updated 2023)

Taylor Malahoff | Nov 10, 2020
Reading Time: 12 minutesDo you find yourself running to Google each time you need something defined? Don’t worry! When I was just starting at a university, I had the exact same problem. My teachers would be throwing out terms that might have been familiar to them but were in another dimension for me.
Having graduated and mastered common business language, I decided to make a list for small business owners of the most commonly used ecommerce jargon they might hear.
1. Abandonment
This usually refers to cart abandonment (when customers come to your website, add something to their cart, but don’t complete the purchase). They essentially abandon their cart—and your website—to do something else.
Because you can usually capture their email before they abandon, you can send them abandonment emails to try to convince them to complete their purchase.
2. Above the Fold
This phrase refers to everything a visitor can see without having to scroll down when your website loads. Having important items above the fold guarantees that customers will always see them.
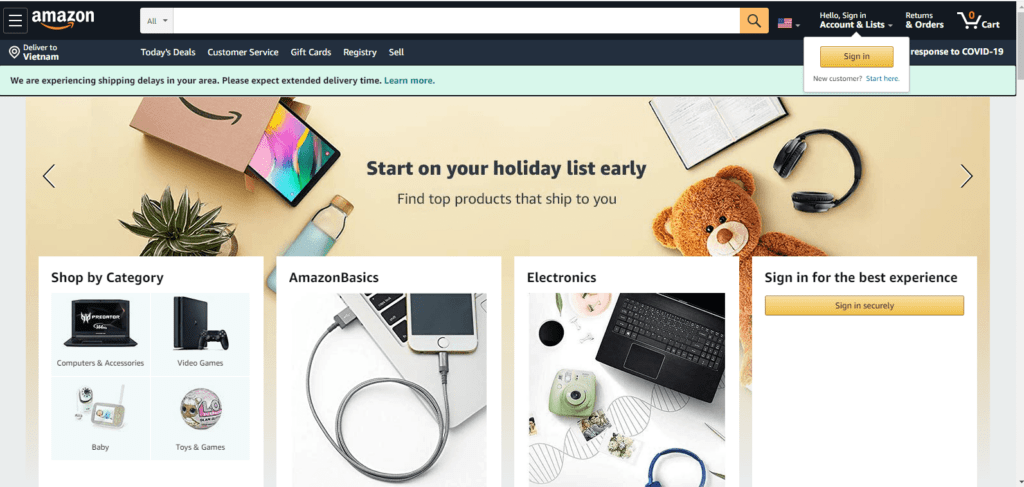
Everything above the fold on Amazon.com when you load the site but haven’t yet scrolled
3. A/B Testing or Split Testing
This is the testing process at the core of conversion rate optimization. During an A/B test, you try two versions of a webpage to see which one “wins.”
For example, say you have a banner on your homepage and you want to try a new banner. Version A shows the original banner, and version B shows the new one. Presenting A to some visitors and B to others lets you compare the performance results of the two versions to determine which one is more successful.
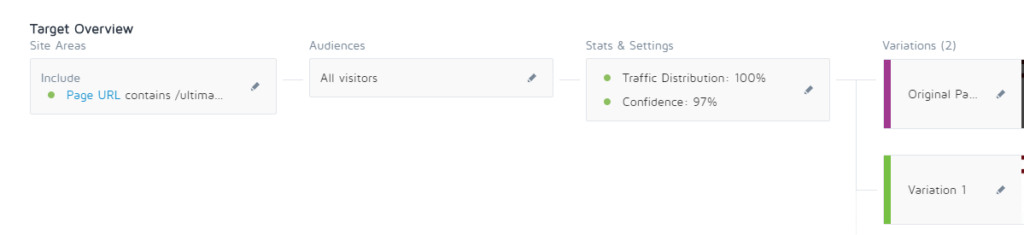
An A/B test dashboard on Convert.com
4. Affiliate
An affiliate is a person or business that sells your products on their own website. They take a small percentage of that sale—a commission-—to make a profit.
With affiliate marketing, a person or business directs customers to your website in order to make a sale. They also receive a commission.
5. Average Order Value (AOV)
The average order value is a Google Analytics metric. It is calculated by dividing the revenue by number of orders. This metric is extremely valuable when you’re trying to figure out if customers are buying more than one product from your store.
Increasing your AOV improves profitability so it’s a metric you should be using to optimize your website.
6. Bounce Rate
The bounce rate is shown as a percentage in Google Analytics. It’s another important metric that measures customers who visit only a single page on your site without doing anything else on that page. The bounce rate can tell you if your page is effective at attracting customers attention and moving them through the process to make a purchase.
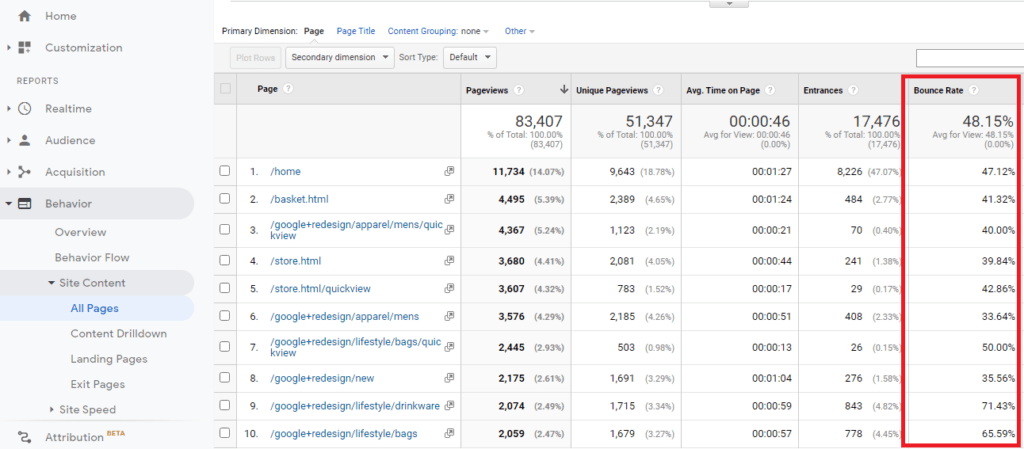
Google Analytics bounce-rate percentage
7. B2C and B2B
B2C (business to consumer) describes selling directly to individual customers. B2B (business to business) describes selling directly to other businesses. Both are very common terms used to describe to whom your business sells.
8. Buy-to-Detail Rate
The buy-to-detail rate is a Google Analytics metric that measures unique purchases by the number of views of the product details page.
This helps you figure out which product people buy most after looking at your product details.
9. Cache
This is the stored data on your computer that makes requests (such as page loading) faster. If your computer already has cached information about a website, then it will load faster than if you are visiting that website for the first time.
Sometimes, you need to delete your cached information to be able to view important changes on your website.
10. Call to Action (CTA)
Calls to action are the words or phrases at the bottom of your homepage banner, emails, product page, collection page, or cart. These are typically buttons that you want customers to click, such as “Add to Cart,” “Continue to Checkout,” “Discover Our Clothes,’ and more.
Calls to action should be one of the most prominent things on your website so that customers don’t miss them.
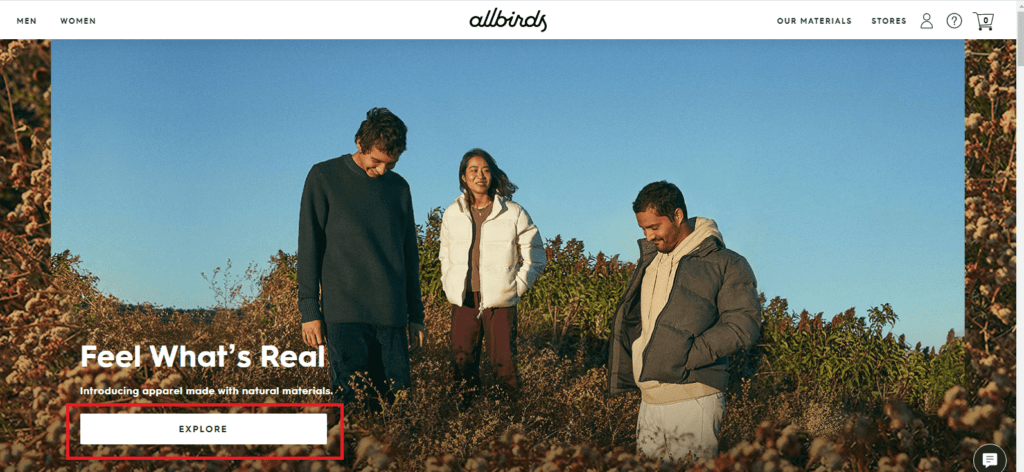
Explore calls to action on Allbirds.com
11. Cart
The cart refers to the cart page on an ecommerce website. It can also be referred to as the bag. This is taken from shopping in real life where you add items to your cart or bag. The cart page is usually a way for your customers to see the total cost of items before they purchase.
12. Churn Rate
This refers to the number of subscribers that unsubscribe during a period of time. If you have a high churn rate, then it means your customers are not enjoying your subscription products and you probably need to look into your product offer or quality.
13. Click-Through Rate (CTR)
Click-through rate is an important metric that measures how many people click through your ad to your website. Having a high CTR means that a lot of people are clicking and are interested.
Checking CTR for clicks to the page with bounce rate to see if customers stay on the page can help you determine if people are enjoying your offer.
14. Cohort Analysis
This involves separating people into groups based on the attributes that they share and then analyzing their behavior. This helps you figure out long-term trends based on your findings about customers.
15. Conversion Funnel
A conversion funnel is the process a customer goes through to make a purchase on your website.
At the top of the funnel, you have someone who comes to your site via an advertisement or an affiliate. At the bottom of the funnel, you have a customer actually making a purchase.
The closer customers are to the bottom of the funnel when they first enter your site, the more likely they are to purchase or perform the action you want them to take.
16. Conversion Rate (CR)
A conversion rate is a metric. It’s calculated by dividing the number of people who convert by the number of customers who visit your website.
A conversion can be clicking a button, purchasing, signing up for an email, and more. It doesn’t always have to be about customers making purchases. For example, if you’re working on your product page, your “Add to Cart” button is the best metric to use, so you’ll want to check the conversion rate for that.
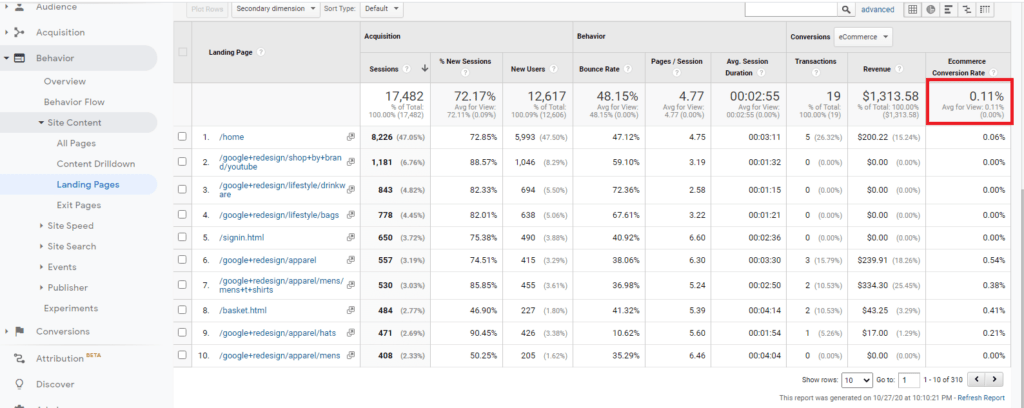
Terrible landing-page conversion rate
17. Cookies
Cookies are small pieces of information stored by your web browser. These help to track your browsing behavior and store vital information such as passwords and usernames so you don’t have to input them each time you visit a website.
18. Cross-Selling
You are cross-selling when you show existing customers another product that they might be interested in buying. This can help improve your overall AOV (average order value). It can also help turn a customer who might not like an initial product into a buying customer.
19. Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Calculate this metric by dividing the total amount of money spent acquiring customers by the number of customers you acquire. CAC tells you how much you’re spending on marketing and related expenses to get a customer who purchases. Having a high CAC will ruin your business, so it’s best to keep this number as low as possible.
20. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
A customer lifetime value refers to the profit you receive from a single customer over the entire time that they are your customer. Knowing CLVs helps you measure your retention of customers and project your overall profitability in the long run.
21. Discount Code
These codes are generated for customers so that they can get a dollar amount or percentage off the price they pay for your product. Discount codes are very valuable for any effort to entice customers to come back after abandonment or to persuade customers to make their first purchase. They’re also useful for holidays and other promotions.
22. Drop-shipping
Drop-shipping is a business model in which you don’t hold any physical inventory. Instead, you sell items and the orders go directly to the manufacturer or wholesaler who then sends the items on to customers.
Because you don’t have to invest a lot of money in inventory at the start, this model is great for when you first want to start up and test the market. However, the profit margins are lower than for other business models.
23. E-book
This digital book can be downloaded easily. It usually comes in PDF format.
E-books are great for adding onto existing products or to capture customer email addresses by giving them a free e-book.

An e-book on Amazon Kindle
24. Engagement Rate
The engagement rate metric shows how many customers have seen your content and have gone ahead and done something with it, such as like, share, or comment.
Having a high engagement rate for your ads means that a lot of people are seeing and interacting with them. This also tells advertising platforms that this content is something people engage with a lot, which could help reduce your advertising costs because the platform is more likely to show this over competitors. (The algorithm for showing ads is quite complicated, but the high engagement increases the relevant ad score and therefore reduces the cost of advertising.)
25. Evergreen Product
An evergreen product is one that consistently makes money without ever dying out. Examples include toothpaste, toilet paper, and food. People have to buy these products regularly, and the products are a necessity.
26. Fulfillment
When you fulfill an order, you are shipping and delivering a product to your customers. Usually, you’d have a fulfillment warehouse that packages and ships your product for you. This is something like what Amazon offers. You can also fulfill the shipment yourself with your own business warehouse.
27. Google Analytics (GA)
Google Analytics is the king of numbers. GA helps your business measure many important metrics so that you can make insightful changes to your website as well as to figure out what’s not performing as it should.
It’s essential that you have some form of analytics. Most stores use Google Analytics. If you aren’t, then I strongly recommend you create an account and install GA right now.
Google Analytics homepage! Start for free.
28. Hashtag
People use hashtags (such as #instafamous #IAmTheBest) to categorize posts on social media platforms.
You’ll want to use hashtags to make sure your posts on Twitter and Instagram are seen by people relevant to your business—ones who are interested in those categories. But don’t add too many, or your post will be seen as spam and not shown as often.
29. Information Scent
When you provide a small amount of information in order to get a customer to click a button to show even more information, that’s information scent. For example, a tab labeled “Shipping” gives enough information that customers will want to click on it to read more about your shipping policies.
30. Key Performance Indicator (KPI)
Key performance indicators are the metrics that show exactly how your website is doing. For revenue optimization, these can be average order value, ecommerce conversion rate, average page load speed, bounce rate, and revenue.
You should have KPIs for each of your endeavors, such as advertising and site optimization.
31. Keyword
A keyword helps search engines categorize your posts or content. When a user searches a specific word in Google, it returns your content to that user if you used the keyword they were looking for.
Be careful though: using the same keyword over and over again tells search engines that your content is spam and will lower your rank within search results.
32. Landing Page
A landing page is the page on your site where customers first arrive. For example, if a customer sees an advertisement about your clothing product and clicks on it, then it will send them to a landing page. This could be your homepage, a category page, or even the product page itself.
Knowing your most popular landing pages is useful. When you see where your traffic is arriving first, you can optimize those pages so customers stay engaged and remain on your website.
33. Lead
A person interested in buying your product or service is a lead. Being able to generate good leads facilitates the buying process. You don’t want to contact people who aren’t interested in your product.
34. Long-Tail Keyword
A long-tail keyword is a long phrase that encourages search engines to show your content to customers who are searching for something specific.
Usually, longer phrases have lower counts for views but also higher conversion rates. This is because the content is more relevant.
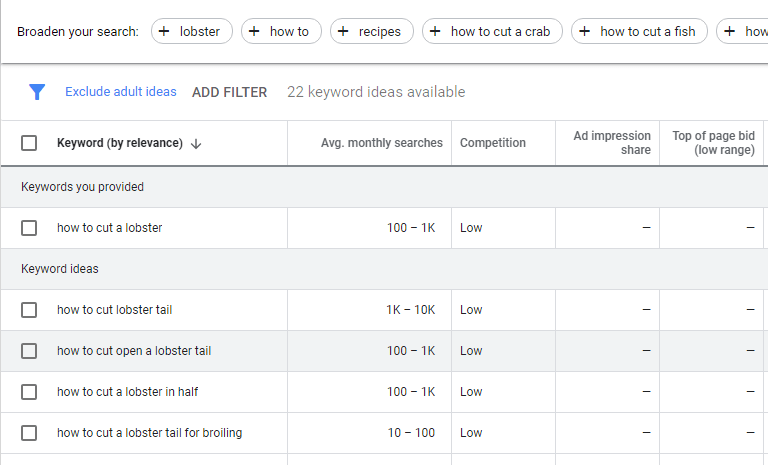
Long-tail keywords for lobsters!
35. Open Rate
Open rate is a metric used in email marketing. The term refers to the rate at which people see your email and decide to open it. Calculate it by dividing the total number of opened emails by the total number of emails sent.
If you have a low open rate, try testing different headlines with your email marketing.
36. Page Views (PV)
This one is pretty self-explanatory. Page views are the number of views that a page has received.
This isn’t based on the number of individual customers who have viewed a page. Page view counts include multiple viewings of a page by a single customer.
37. Payment Gateway
A payment gateway is the payment provider’s method of processing your customers’ transactions. Popular gateways include PayPal, Klarna, Amazon Pay, GooglePay, and Apple Pay.
I recommend having PayPal on your website, at least, to increase the number of conversions on your checkout. PayPal is well trusted.
38. Pay-per-Click (PPC) or Cost-per-Click (CPC) Advertising
PPC and CPC advertising refer to the same thing: paying an advertising platform such as Google, Facebook, or Twitter for clicks. This is the most commonly utilized source of advertising on the internet. Understanding the cost you pay per click and comparing that to the revenue you generate from your sales helps you determine if your advertising is or isn’t worth the cost.
Facebook Ads dashboard
39. Profit Margins
Profit margins are calculated by first subtracting your total expenses from your total revenue. Then divide the resulting number by your total revenue.
A 40% profit margin is really good—the higher the better. Calculating your profit margins helps you understand if it’s actually worth selling a particular product.
40. Return on Investment (ROI)
This metric is calculated by taking your gain of the investment and then subtracting the cost of that investment. Divide the resulting number by the cost of the investment. If your ROI is 50% and your initial investment is $2000, you should get back $3000 at the end of the process.
ROI helps to determine if you are investing correctly and will also help you optimize your advertisements. Don’t solely base your decisions on ROI alone though.
41. Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
This is the optimization process of making sure your website or content is showing up on search engines. The higher you rank on the list of search results, the more people you’ll have coming to your website.
Optimization can be done with keyword ranking, backlinks, meta tags, and other forms of search engine optimization. You won’t see results right away, but it’s more of a long-term plan.
42. Search Engine Results Page (SERP)
The search engine results page is what you see after you search for a word or phrase on a search engine (like Google). At the top of the SERP, you’ll see the paid search results; farther down the page, you’ll see the results that have not been paid for.
You want to be ranking as high as you can on these pages to drive people to your website.
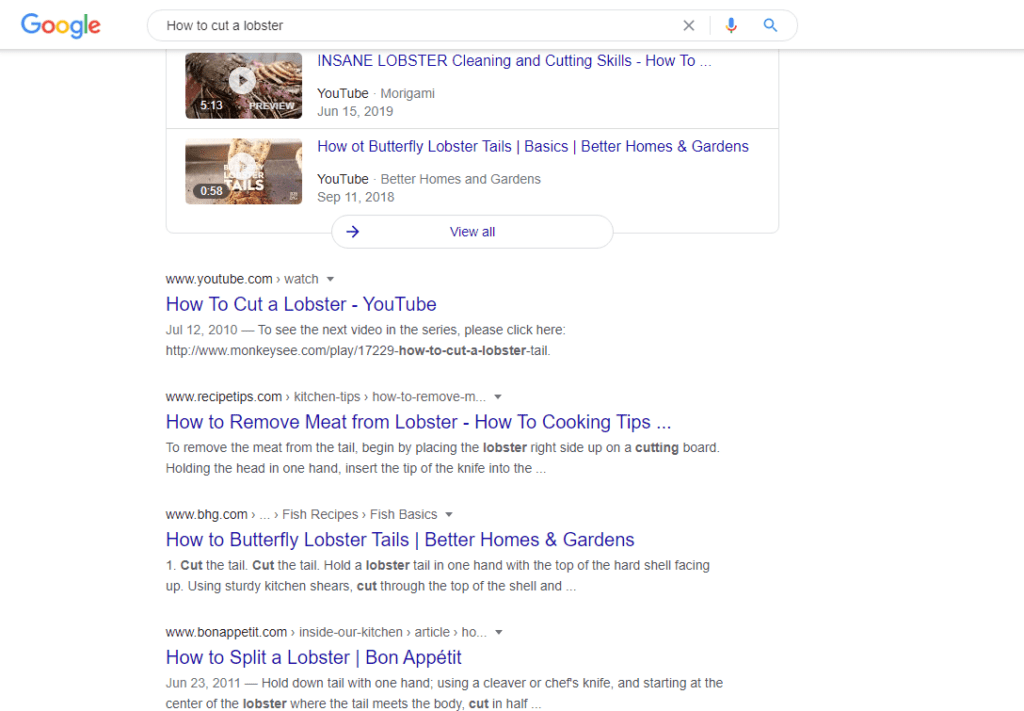
Search engine results for “How to cut a lobster”
43. Social Proof
Social proof is what you show customers to indicate that your product or service is being used by other customers. For example, a photo of a celebrity using your product. can create a massive amount of social proof whereas if a celebrity is using it then it must be great.
44. Software as a Service (SAAS)
Software as a service refers to renting software via a subscription. This is a unique business model that’s usually used in B2B situations but can be used in B2C situations as well.
Most Shopify apps are SAAS companies as they provide their app as a subscription.
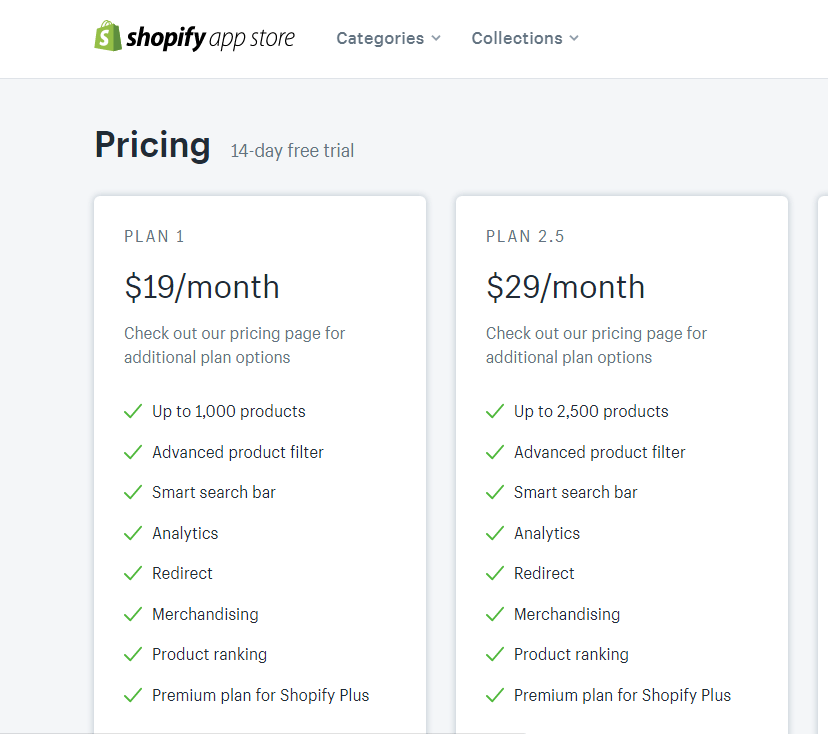
Subscription plans for using a Shopify app
45. Stock Keeping Unit (SKU)
SKUs are codes used on the backend of your store for shipping purposes. These help to identify which product needs to be shipped and to keep track of inventory.
Don’t show your SKUs on your website as customers don’t need to see them.
46. Unique User
A unique user is a who is counted only once regardless of how many times that user revisits your website.
This is an important number to compare to results. If you use just the “user” metric in Google Analytics, it also includes multiple revisits by the same user. You should always compare using unique users.
47. Upselling
When a customer purchases an item or adds an item to the cart, you upsell by providing them with another product that goes with it or offering a bundle. For example, at McDonald’s you’re always asked if you want your fries supersized. This is an upsell from the regular-sized item.
48. URL (Universal Resource Location)
A URL is the address or location of your website. For example, “www.buildgrowscale.com” is a URL.
Conclusion
I hope that these definitions are helpful. You can always refer to this list when you need it, but eventually using ecommerce jargon will become effortless and you won’t need a list at all.
If you are looking for conversion tweaks that will double your Shopify store’s performance almost instantly, then click here!



Table of Contents
1. Abandonment2. Above the Fold3. A/B Testing or Split Testing4. Affiliate5. Average Order Value (AOV)6. Bounce Rate7. B2C and B2B8. Buy-to-Detail Rate9. Cache10. Call to Action (CTA)11. Cart12. Churn Rate13. Click-Through Rate (CTR)14. Cohort Analysis15. Conversion Funnel16. Conversion Rate (CR)17. Cookies18. Cross-Selling19. Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)20. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)21. Discount Code22. Drop-shipping23. E-book24. Engagement Rate25. Evergreen Product26. Fulfillment27. Google Analytics (GA)28. Hashtag29. Information Scent30. Key Performance Indicator (KPI)31. Keyword32. Landing Page33. Lead34. Long-Tail Keyword35. Open Rate36. Page Views (PV)37. Payment Gateway38. Pay-per-Click (PPC) or Cost-per-Click (CPC) Advertising 39. Profit Margins40. Return on Investment (ROI)41. Search Engine Optimization (SEO)42. Search Engine Results Page (SERP)43. Social Proof44. Software as a Service (SAAS)45. Stock Keeping Unit (SKU)46. Unique User47. Upselling48. URL (Universal Resource Location)ConclusionTable of ContentsAbout the authorLeave a Comment Cancel ReplyAbout the author
Taylor Malahoff
Taylor Malahoff is currently a Revenue Optimization Expert at Build Grow Scale. He graduated from the University of Northern British Columbia with a Bachelor’s in Marketing and works remotely from the digital nomad hub of Vietnam. Not only does he manage a 7-figure store, but he enjoys market research and conducting A/B tests to address concerns. Taylor Malahoff loves great food. One of his more unusual dishes he has tried is Sanakji, which is chopped up octopus tentacles, a delicacy in South Korea.



